how do glasses work physics
If you close one eye and hold. Glasses with Polarizing Filters.
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light
Glasses are comprised of lenses that bend light.

. Our eyes detect colors using cones. How do Glasses Work Physics. The third way your brain percieves distance is it gauges the lenses in your eye.
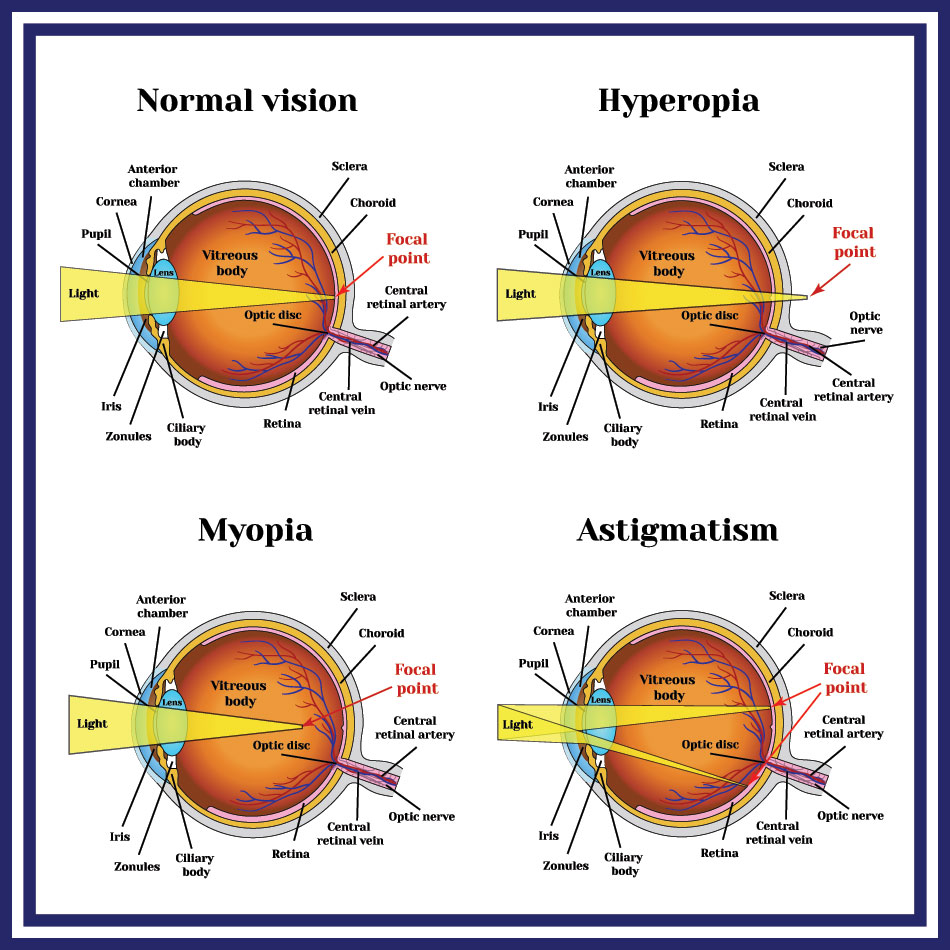
Glasses are cut to change the focal length of the light entering the eye so it hits the focal point properly and the wearer can see without blurring. Behind this work physics plays a vital role in altering the focal length of the light entering the eye. Because of the different wavelengths of light each.
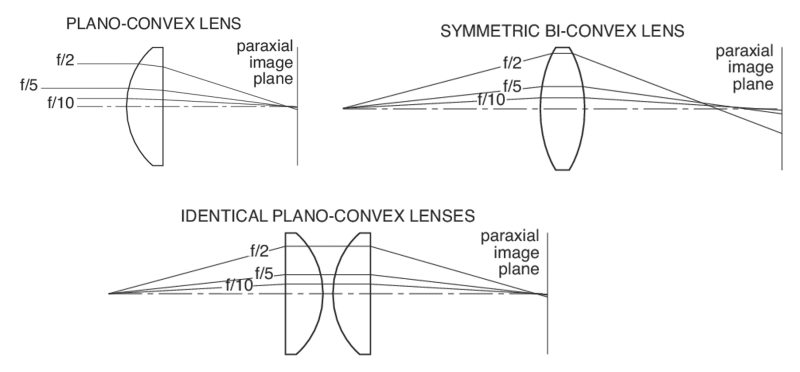
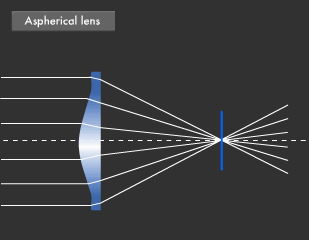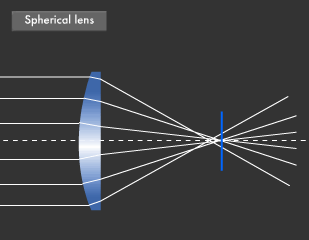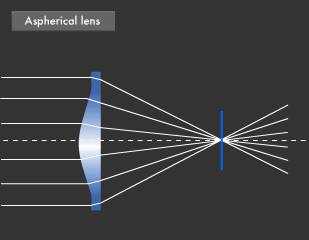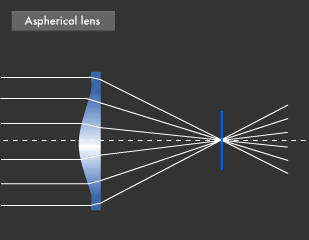
Convex lenses are refracting the light from the bottom top of the. Light hits the glass at an angle and it gets refracted towards the centre. Cornings deep understanding of optics helps shed.
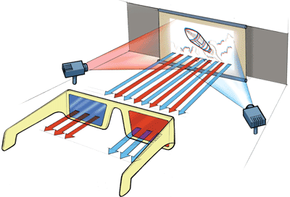
In a movie theater the reason why you wear 3-D glasses is to feed different. It uses the slower speed of light in glass to its advantage by refracting the light twice. Most of us think.
The lens of the eye will need to compensate for closer objects. Light in areas even the eye cant see. How do glasses use waves to work.
The red and blue lenses filter the two projected images allowing only one image to enter each eye. Optical physics is the study of light and its interaction with matter. This in turn becomes a measure of how far away an object is.
These glasses are used when two images are projected superimposed onto the same screen through. How do glasses work physics Monday April 4 2022 Edit The eyeglass lens is simply used to create an image of the object at a distance where the nearsighted person can. For glasses that correct for near sighted people this also means a reduction in size of the image on the retina.
Glasses help the wearer to see clearly and make the focal point ideally. The eyeglass lens is simply used. A magnifying glass is usually a convex lens a lens that bulges outwards made of either glass or plastic.
There are three types of cones. In these there are two types Linearly Polarized Glasses. S M and L and they are responsible for identifying the colors blue green and red respectively.
When a beam of light passes through any curved piece of glass it has a tendency to either expand the beam and spread it.
3 D Viewing How 3 D Glasses Work Howstuffworks
Canon Canon Technology Canon Science Lab Lenses
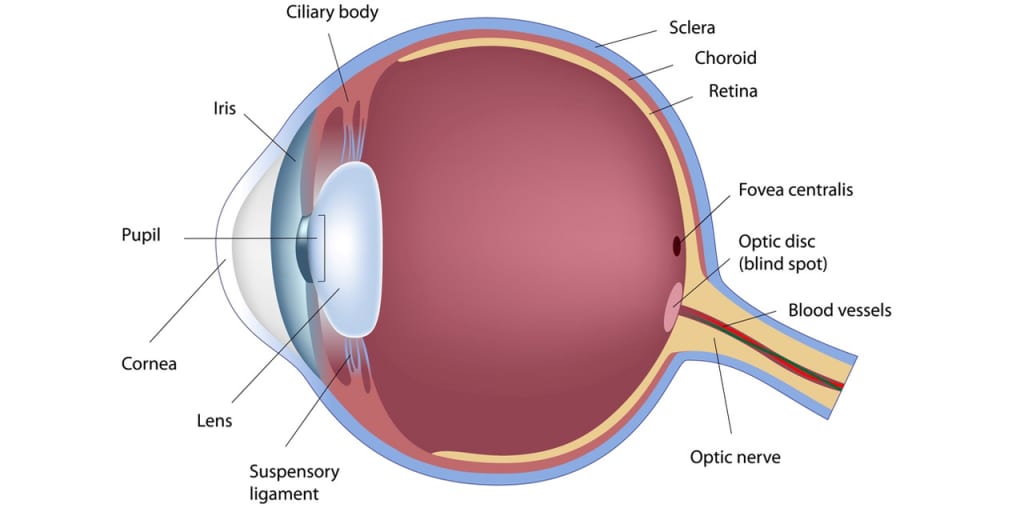
The Science Of Eyeglasses Williams Eye Works

Vision Correction Physics Course Hero
26 2 Vision Correction College Physics Chapters 1 17
What Is The Physics Behind Corrective Eyeglasses Quora
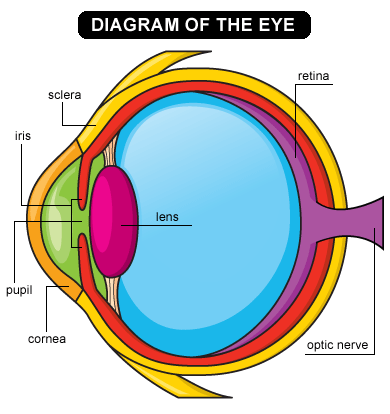
Glasses And Contact Lenses For Kids Nemours Kidshealth
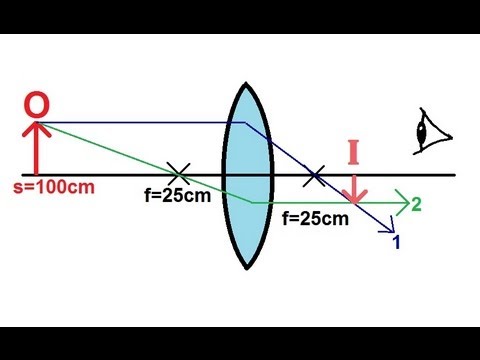
Physics Optics Lenses 1 Of 4 Converging Lens Youtube
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

Corrective Lenses For Eyes Glaza
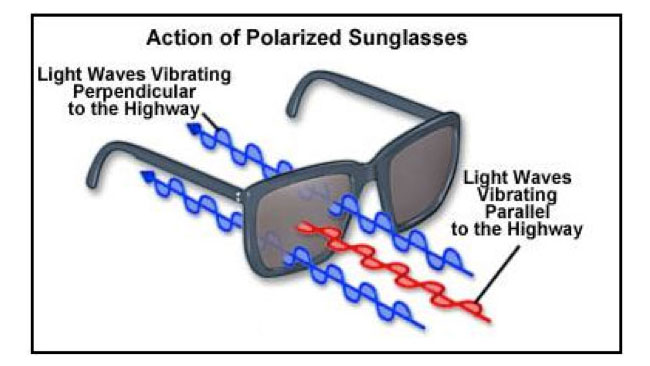
The Physics Of Polarizing Filters
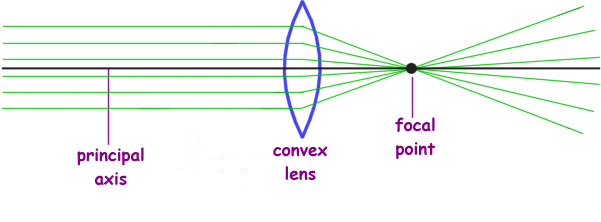
Physics For Kids Lenses And Light
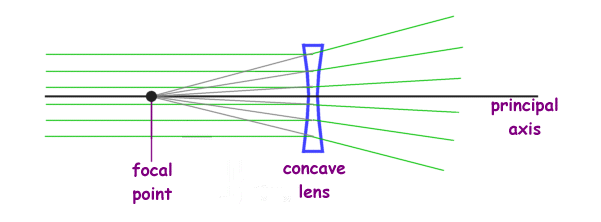
Physics For Kids Lenses And Light
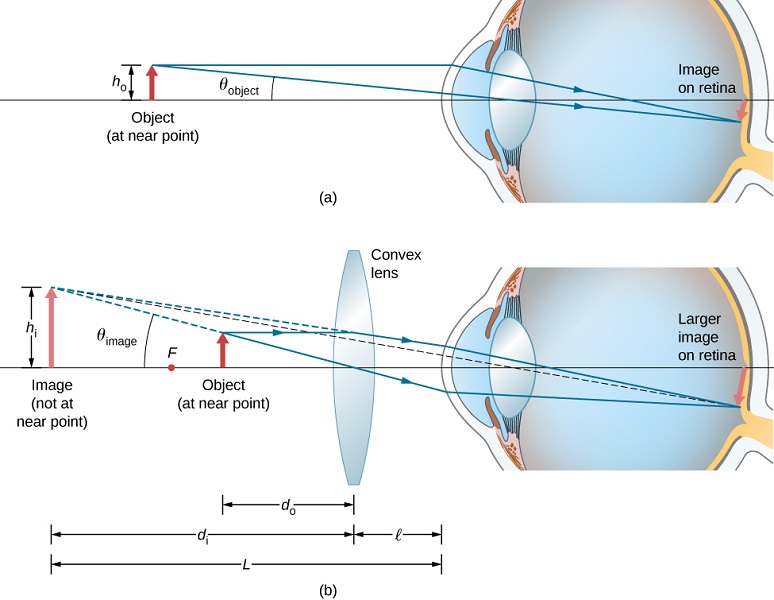
2 8 The Simple Magnifier Physics Libretexts